What effect does the peeling strength have on the use of tarpaulin
What effect does the peeling strength have on the use of tarpaulin
The peeling strength (or adhesion strength) of a tarpaulin—the force required to separate its laminated or coated layers—directly impacts its durability, weather resistance, and lifespan. Here’s how insufficient peeling strength affects performance:
1. Delamination & Structural Failure
Weak peeling strength causes layers (e.g., PVC coating and polyester fabric) to separate under stress.
Result: Cracks, bubbles, or flaking, exposing the fabric to damage.
2. Reduced Weatherproofing
Water leakage: Delaminated areas allow water seepage, defeating waterproofing.
UV degradation: Exposed fabric fibers weaken under sunlight, fading colors and reducing strength.
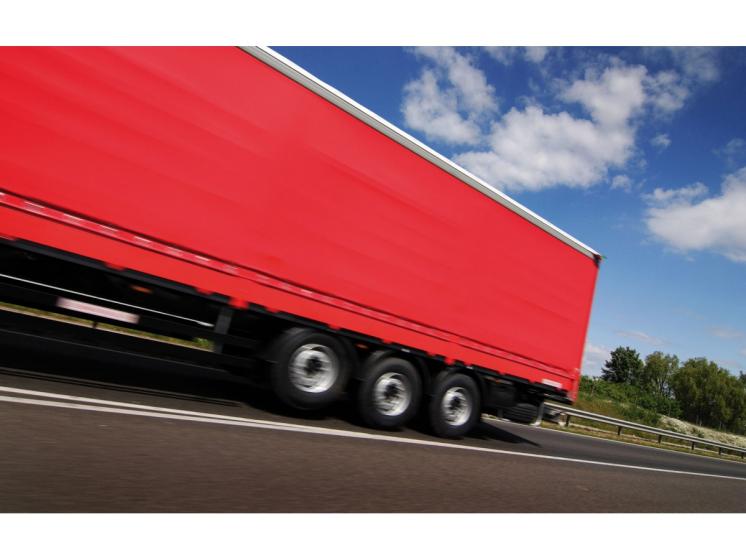

3. Poor Tear/Puncture Resistance
The coating reinforces the PVC tarpaulin fabric; peeling weakens this bond, making the tarp easily torn by wind, sharp objects, or heavy loads.

4. Shortened Lifespan
Accelerated wear: Peeling spreads over time, leading to premature failure.
Costly replacements: Tarps degrade faster, increasing long-term expenses.
5. Critical Application Failures
Truck covers: May rip open during transit.
Industrial curtains: Lose flame/chemical resistance if layers separate.
Awnings: Collapse risks in storms due to weakened seams.
Causes of Low Peeling Strength
Poor-quality adhesives or uneven coating during manufacturing.
Incorrect temperature/pressure in lamination.
Low-grade fabric or PVC mix.
Solutions to Improve Peeling Strength
Material Selection:
Use high-density fabrics (e.g., 1000D polyester) with strong PVC coatings.
Opt for laminated tarps (not just coated) for heavy-duty use.
Manufacturing Controls:
Ensure proper heat, pressure, and adhesive application during production.
Testing & Standards:
Verify peeling strength via ASTM D751, ISO 2411, or DIN 53357.
Look for tarps with ≥50 N/cm peeling resistance for demanding applications.
When Does Peeling Strength Matter Most?
Outdoor use: High winds, UV exposure, and rain demand strong adhesion.
Industrial loads: Tarps covering sharp-edged cargo or machinery.
Long-term installations: Permanent canopies, stadium roofs, or marine covers.